ABOUT HUNTİNGTON'S DİSEASE
Summary
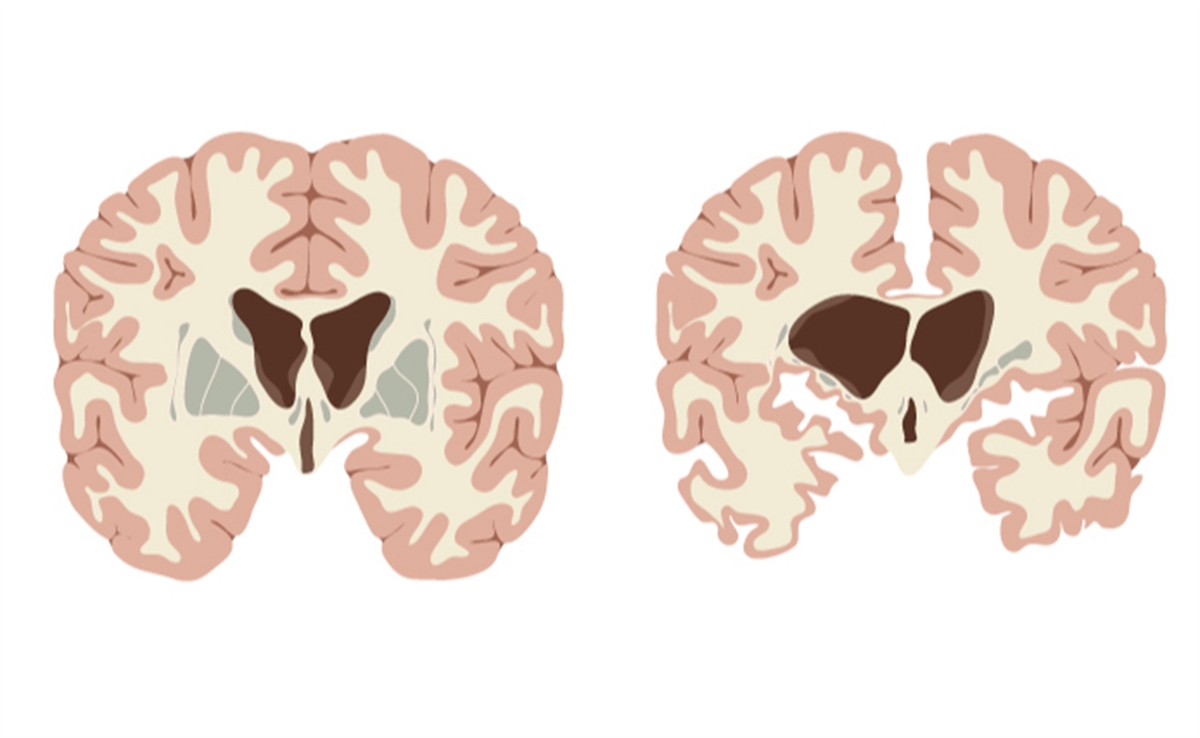
Huntington's disease (HD) is a hereditary disorder that leads to the loss of specific nerve cells in the brain. Individuals are born with a defective gene, but symptoms typically manifest in middle age. Early signs of HD include involuntary movements, clumsiness, and balance issues. In advanced stages, the disease can completely impair walking, speaking, and swallowing abilities. Some patients may lose the ability to recognize family members, while others remain aware of their surroundings and can express their emotions.
If one of your parents has Huntington's disease, your risk of developing the condition is 50%. A blood test can determine if you carry the HD gene and your likelihood of developing the disease. Genetic counseling can help you weigh the risks and benefits of undergoing the test.
There is no cure for Huntington's disease. Medications can help manage some symptoms, but they cannot slow down or stop the progression of the disease. Therefore, individuals living with HD and their families often turn to various supportive treatments and strategies to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Psychiatric Symptoms
- Apathy, sadness, or irritability
- Social withdrawal
- Insomnia
- Loss of energy and persistent feelings of fatigue
- Frequent thoughts of suicide and death
What Are the Treatment Methods for Huntington's Disease?
There is no definitive cure for Huntington's disease, but medications can be used to manage its symptoms. These medications are adjusted based on the progression of the disease and may have side effects. Medications used to control involuntary movements can increase restlessness and depression. Antipsychotic drugs may be added to the treatment to mitigate these side effects. Antidepressants are used for psychiatric disorders, but they too can cause side effects. Psychotherapy is recommended to cope with behavioral problems. Speech and physical therapy are also included in the treatment methods. These treatments aim to improve the patient's quality of life and help manage symptoms. However, the progression of the disease cannot be halted, and the treatment is focused solely on symptom management.
### Synaptic Modulation: Neflamapimod
Neflamapimod is a small molecule that can penetrate the brain and acts as an inhibitor of the p38-alpha enzyme. This enzyme plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation, and chronic activation can lead to excessive inflammation that negatively impacts neuronal communication.
Various studies on animal models, particularly mice, have shown that neflamapimod has the potential to reverse synaptic dysfunction, suggesting its usefulness in treating neurodegenerative diseases like Huntington's disease (HD).
Based on these findings, the current clinical trial (NCT03980938) aims to investigate whether neflamapimod can reverse hippocampal dysfunction in early-stage HD patients. This trial seeks to test neflamapimod's synaptic modulation capability in a clinical setting, assessing its potential as a treatment method for HD.
### Antibody Therapy: ANX005
ANX005 is a monoclonal antibody designed to inhibit C1q, the initiating molecule of the complement pathway of the innate immune system. The complement system serves as a primary defense mechanism against infections, but its overactivation can be harmful in neurodegenerative diseases.
Currently, the safety and tolerability of ANX005 are being evaluated in individuals with manifest Huntington's disease or those at risk of developing the disorder (NCT04514367). This study is a significant step in determining whether ANX005 can be a potential treatment option for HD, examining its effectiveness in slowing disease progression or alleviating symptoms.
What Are the Treatment Methods for Huntington's Disease?
There is no definitive cure for Huntington's disease, but medications can be used to manage its symptoms. These medications are adjusted based on the disease's progression and may have side effects. Medications used to control involuntary movements can increase restlessness and depression. Antipsychotic drugs may be added to the treatment to mitigate these side effects. Antidepressants are used for psychiatric disorders, but they too can cause side effects. Psychotherapy is recommended to cope with behavioral problems. Speech and physical therapy are also included in the treatment methods. These treatments aim to improve the patient's quality of life and help manage symptoms. However, the progression of the disease cannot be halted, and the treatment is focused solely on symptom management.
Conclusion
Huntington's disease is a genetic disorder with no cure, leading to severe and progressive neurological, cognitive, and psychiatric impairments. Early diagnosis and proper management can improve patients' quality of life and reduce symptom severity.
Comments
Post a Comment